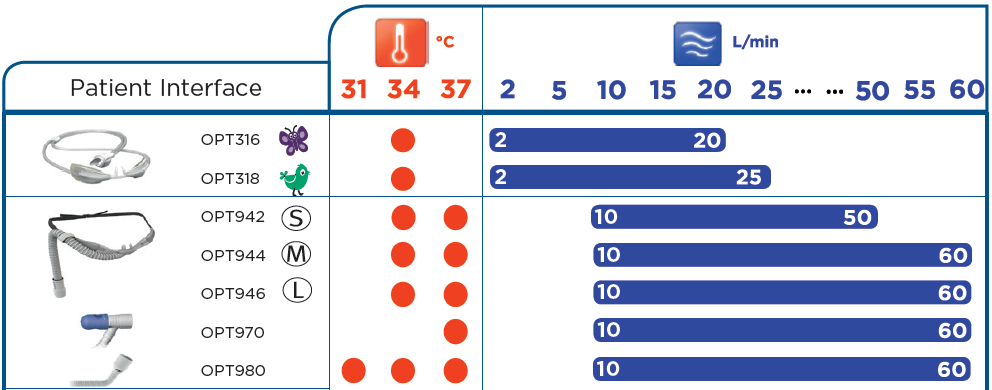
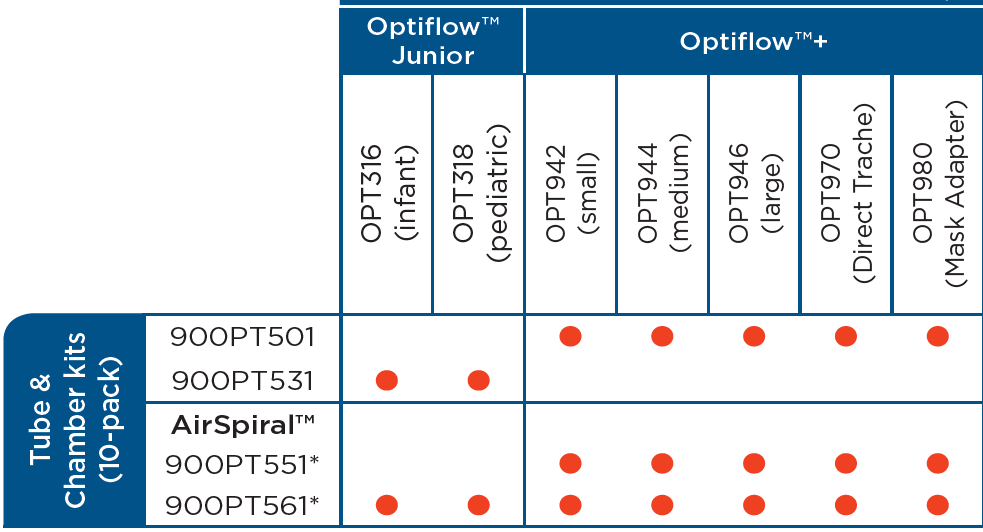
oxygen delivery devices and flow rates australia
Depending on a patients inspiratory effort tidal volume speed of inspiration and respiratory rate the PIFR can often exceed the flow rate at which oxygen or an oxygenair mixture is supplied by the device meaning that at the time of PIFR. Oxygen delivery devices 1.
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery
Results OxyMask was effective at supplying a wide range of FiO 2 values at various flow rates.

. MORS with an oronasal or intraoral mask demand valve with an intraoral mask and NRB at a flow rate of 15 Lmin¹. The fixed performance devices were assessed using the oxygen flow rates for the appropriate inserts as. 4060 FiO2 at a flow of ³5 Lmin Delivery of higher FiO2 levels than nasal cannulae.
Oxygen to patients under a variety of flow rates. Watch this short video for an easy to understand description of some of the most common oxygen delivery devices you will see in the clinical setting and on y. Documented hypoxemia In adults children and infants older than 28 days arterial oxygen tension PaO2 of 60 mmHg or arterial oxygen saturation SaO2 of 90 in subjects breathing room air or with PaO2 andor SaO2 below desirable range for specific.
High-concentration normobaric oxygen O₂ administration is the first-aid priority in treating divers with suspected decompression illness. The MR 81070 shall define the target oxygen saturation oxygen therapy delivery device range for oxygen flow or percent of inspired oxygen and when oxygen is to be applied. Methods This was a prospective observational study where healthy volunteers used OxyMask at escalating oxygen flow rates.
Of the commonly available devices promoted for O₂ delivery to injured divers similar PtcO₂ and nasopharyngeal F I O₂ values were obtained with the three devices tested. Non-rebreather reservoir mask 60 FiO2 at a flow of 15 Lmin. The prescription shall be reviewed daily 9.
These devices deliver a variable inspired oxygen concentration to the patient which depends on the PIFR. A regulator is attached to the cylinders top and works like a tap allowing the safe adjustment of oxygen flow rate provided in Lmin 1. To determine whether administering O₂ with a non-rebreather mask NRB at a flow rate of 10 or 15 Lmin ¹ or with a demand valve with oronasal mask.
The variable performance devices were tested at oxygen flow rates of 2 4 6 8 10 and 15 lmin 1 as delivered by an AHE ball flow meter. Of the commonly available devices promoted for O 2 delivery to injured divers similar P tc O 2 and nasopharyngeal F I O 2 values were obtained with the three devices tested. The recommended initial oxygen flow rate for open-circuit systems employing a non-rebreather mask has long been 15 Lmin-1.
It varies from 0 15L per. Same as Salter with added benefit of providing higher flow rate and. OXYGEN DELIVERY DEVICES Dr.
The prescription shall be signed dated and the name of the prescriber printed legibly. The flow rate can be set on the wall tap. Fraction of inspired oxygen FiO 2 was the main clinical endpoint.
Given typical supply limitations there is a natural interest in reducing the flow rate to extend oxygen delivery duration. Demonstrated oxygen desaturation on oximetry or arterial blood gases at rest on exercise or nocturnal with SaO2 less than 90 or PaO2 less than 60mmHg is required. Comfort cost easy titration.
It is then put through different devices at different rates to adjust the oxygen concentration that the patient inspires. The percentage of oxygen inspired depends on the flow rate and the delivery device. Indications of O2 therapy 1.
Delivery of higher FiO2 than simple mask. 2435 FiO2 at a flow of 14 Lmin. The HFNC is an oxygen-delivery system that includes an airoxygen blender humidifier heater and nasal cannula to deliver precise and very high flow oxygen to your patient.
Domiciliary oxygen and equipment may be provided for adults without. When the tap is manually opened the oxygen takes the line of least resistance to the patient via an oxygen delivery device eg. MORS with an oronasal or intraoral mask demand valve with an intraoral mask and NRB at a flow rate of 15 Lmin-1PtcO2 and nasopharyngeal F I O 2 values were.
Different oxygen flow rates result in a highly variable and unpredictable FiO 2 Rebreathing of CO 2 can occur with O 2 flow rates of less than 2 L O 2 lmin or if minute ventilation is very high 4 Lmin of oxygen flow delivers an FiO 2 of about 03504 providing there is. Oxygen flow rate was controlled via a standard wall-mounted flow rate metre CIG Health Care Comweld Group Pty Ltd Australia with testing conducted at a flow rate of 15 Lmin for all devices and additionally for flow rates of 6 and 8 Lmin when using oxygen tubing. Tube with a mask or nasal cannula.
Subsequently question is which oxygen delivery device provides the lowest concentration of oxygen. The best O₂ delivery device and flow rate are yet to be determined. Oxygen use has extended from inpatient to outpatient settings for patients with chronic pulmonary diseases and complications of hypoxaemia.
Nebulisers and high-flow nasal can nulae HFNC provide oxygen at flow rates adequate 51 enough to meet the inspiratory demands. The nasal cannula is a low flow system that mixes oxygen with room air. High Flow Nasal Cannula.
A pressure reading barometer. Dropping the oxygen flow rate closer to 10 Lmin-1 has been suggested as a compromise but the. The flow rates range from 1 to 6 litersminute providing 24 to 44 of inspired oxygen.
Domiciliary oxygen a nd equipment may be provided for adults with pulmonary arterial hypertension. 25 FiO. The indications advantages and disadvantages of each.
Oxygen is delivered from taps above ward beds at 100 concentration. This article presents an overview of oxygen devices oxygen concentrators compressed gas cylinders and liquid oxygen and delivery systems high- and low-flow.
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery

Providing Supplemental Oxygen To Patients Today S Veterinary Practice
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery

Veal Chop Mine Nursing Google Search Nursing School Notes Nursing School Tips Nursing School

High Flow Oxygen Concentrator Review And Comparison 2021

O Two Single Use Cpap Otwo Com

Efficacy Of High Flow Nasal Cannula Vs Standard Oxygen Therapy Or Nasal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure In Children With Respiratory Distress A Meta Analysis The Journal Of Pediatrics

Preoxygenation Deoxygenation And Reoxygenation During Intubation

Oxygen Delivery By Device Nasal Cannula Indicated For Low Flow Low Percentage Sup Respiratory Therapy Student Nursing School Survival Pediatric Nursing